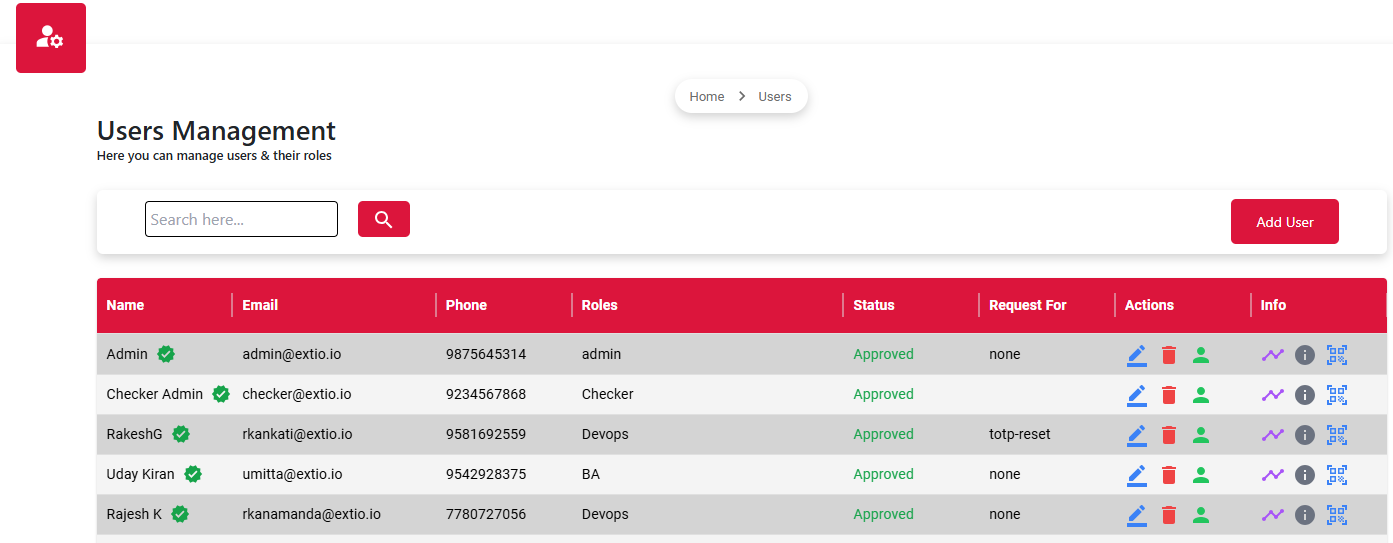
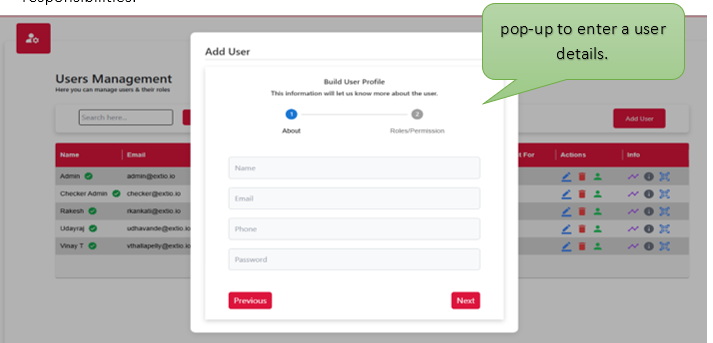
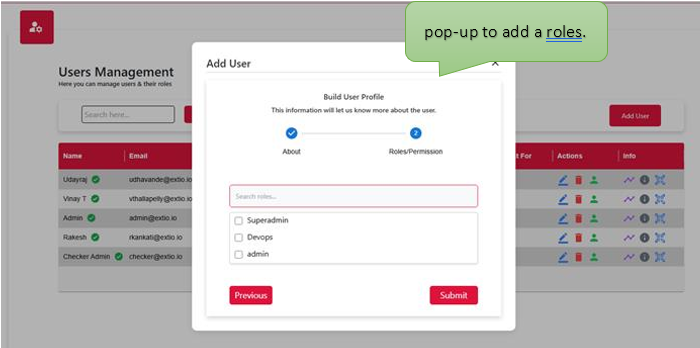
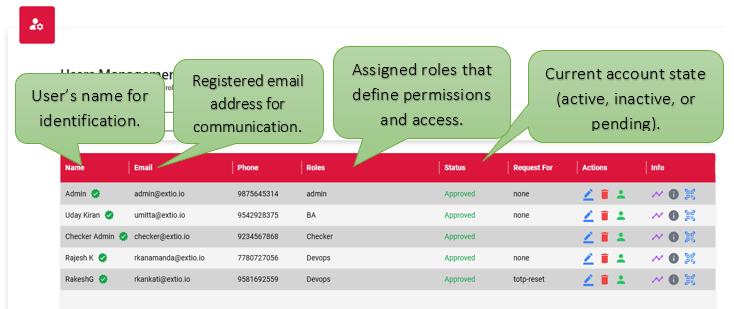
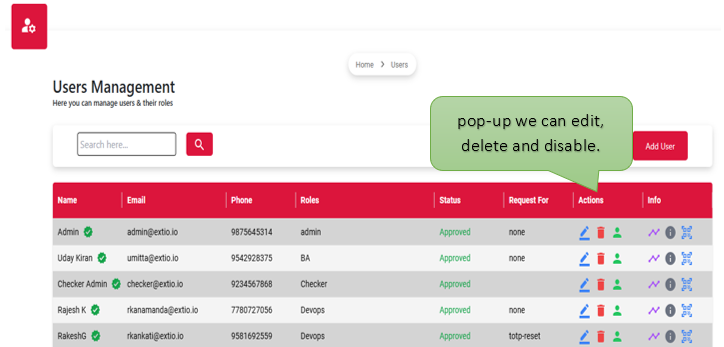
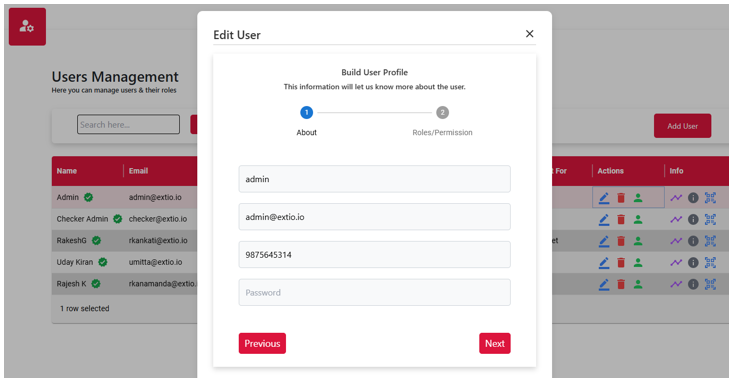
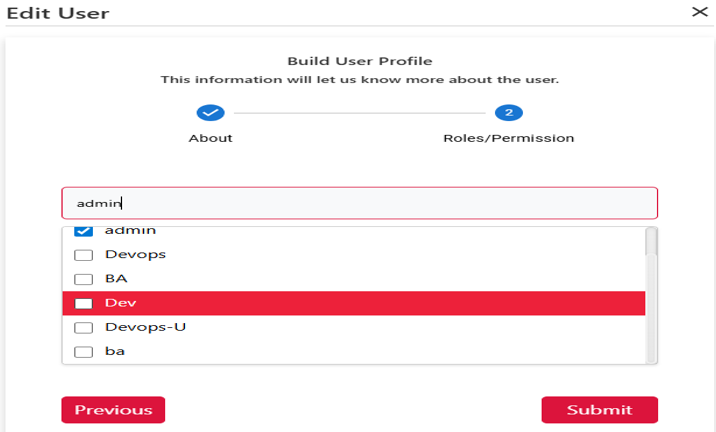
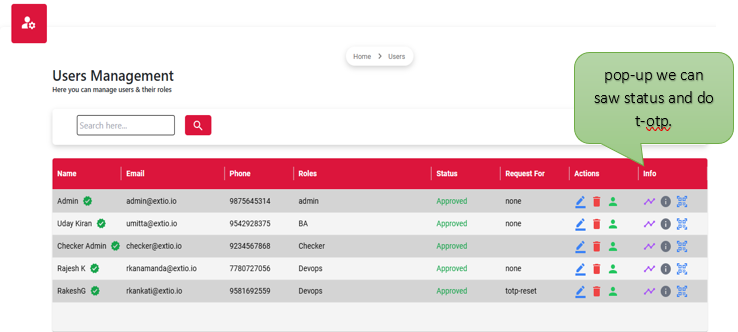
User management roles define the access levels and responsibilities assigned to individuals within a system. These roles determine what actions users can perform, such as creating, editing, or viewing data, and help enforce security, accountability, and proper workflow control. By assigning roles like admin, editor, or viewer, the system ensures users have the appropriate permissions based on their duties, reducing errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
Introduction:
User Management Roles are a fundamental part of access control within any application or system. They define what each user is permitted to do based on their responsibilities such as managing data, performing administrative tasks, or simply viewing content. Assigning roles helps maintain security, structure user interactions, and streamline system operations by ensuring that each user only accesses the features and information relevant to their role.